A Brief History of History
Staring into our past
 Looking up at billions of stars at night can make you feel really small in the universe—but you are also special. We all come from generation after generation of people. They lived, had babies, and passed on their knowledge against difficult odds. Technology helped humans beat those odds. Every species is unique, but our ability to ponder the universe and pass down our knowledge makes us pretty special.
Looking up at billions of stars at night can make you feel really small in the universe—but you are also special. We all come from generation after generation of people. They lived, had babies, and passed on their knowledge against difficult odds. Technology helped humans beat those odds. Every species is unique, but our ability to ponder the universe and pass down our knowledge makes us pretty special.
Archaeology is the study of past human behavior. Scientists study ancient stones and bones to find out how people behaved in the past. The beginning of what is “human” is hard to see because many other early human species existed. Some of our ancestors even made and used stone tools and probably acted very similar to how we act. Did that make them human?
“What does it mean to be human?” is one of the biggest questions that we can ask, and looking back at our history helps us answer that question.
A European dead end
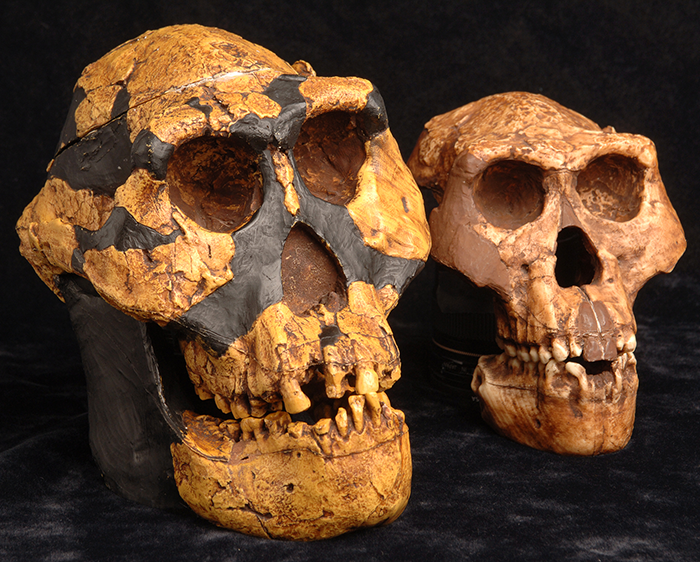
More than 100 years ago, scholars made an unusual discovery in the caves of the Neander Valley in Germany. Bones from a very human-like creature were found alongside stone tools. The skeleton had a lot in common with human skeletons, but it also had some big differences. This creature would have been very strong. The bony ridges above its eyebrows stuck out. It had no chin. And the back of its head was connected to thick neck muscles. It’s been said that if this creature sat next to you on a bus, you’d probably change seats. But this isn’t an alien species: it’s a Neanderthal.

In the late 1800s, there were no methods to determine how old Neanderthal bones were. However, the fact that they were found in lower levels of the ground than human skeletons meant that they were older. This is because older fossil layers tend to be at the bottom and younger towards the top. At the time, scientists thought that this meant humans had evolved from Neanderthals in Europe. The types of artifacts that were found with Neanderthals were thought to align more with nonhuman behavior. The artifacts found with the human skeletons in the upper layers of soil were seen as "modern."
After 150 years of research and discovery, we now know a lot more about where we came from. In the past, most researchers who studied fossils were based in European countries. It was easier for them to do field work nearby, so Europe is where most discoveries were being made. That made it seem as though Europe was where the main events of human evolution had taken place. However, as more and more research was done in Africa, Asia, and Australia, this story changed a lot.
Body fuels the mind
At this point, we need to make a distinction between body and mind. We need to look at how the origin of the modern human body and the origin of modern human behavior are different. The first modern body can be identified from the earliest fossils of Homo sapiens. If brought back to life, an ancient Homo sapien could sit next to you on the bus and you might not notice. But if you tried talking to her, many differences would be clear in a minute! Behavior is much more difficult to determine from the archaeological record, but we’ll come back to that in a second.
The making of modernity
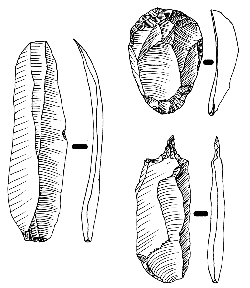 Modern human behavior is hard to pinpoint in prehistory. Traditionally, scientists used European sites to define what modern behavior is and isn’t. From this view, artifacts used by Neanderthals in the Middle Paleolithic, around 100,000 years ago, were not modern. Artifacts used by humans in the Upper Paleolithic, beginning around 40,000 years ago, were modern. For instance, Upper Paleolithic tools contain a large number of blades (stone flakes twice as long as they are wide), tools made from shell and bone, and artwork. Those artifacts are not found at Middle Paleolithic sites where Neanderthals lived.
Modern human behavior is hard to pinpoint in prehistory. Traditionally, scientists used European sites to define what modern behavior is and isn’t. From this view, artifacts used by Neanderthals in the Middle Paleolithic, around 100,000 years ago, were not modern. Artifacts used by humans in the Upper Paleolithic, beginning around 40,000 years ago, were modern. For instance, Upper Paleolithic tools contain a large number of blades (stone flakes twice as long as they are wide), tools made from shell and bone, and artwork. Those artifacts are not found at Middle Paleolithic sites where Neanderthals lived.
But these definitions for modern behavior didn't last that long. The discovery of many types of tools in Africa that are much older than those in Europe changed all of this. We now know that stone blades are found in South Africa at a site called Kathu Pan 1 from about 500,000 years ago. These blades appear to have been attached to wooden handles and used as spears. Ochre, a mineral used to paint symbols, is found at many sites across Africa dating back to around 160,000 years ago. These discoveries in Africa have made us question the timing of the evolution of our bodies and minds. The gap of time between the origin of modern anatomy and of modern artifacts has all but disappeared.
Who do you think you are?
We are the last in a line of tool-using hominins who left Africa to settle all over the world about 50,000 years ago. We live and work well with others others in large groups, including people we are not closely related to. We are really good at learning things and teaching new information to the next generation. The information we pass on to the next generation can become the beginning of new ideas and ways of solving big problems in our society. We can use symbols to communicate complex ideas. We do this by making relationships between unrelated things. But there are still so many other questions about our history that we are only beginning to ask. Why did we become so cooperative? If we are cooperative, why does war still exist and can we do anything about it? Philosophers and scientists are all asking these big questions. Archaeology is beginning to help provide some of the answers.
Bibliographic Details
- Article: A Brief History of History
- Author(s): Benjamin Schoville
- Publisher: Arizona State University Institute of Human Origins Ask An Anthropologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask An Anthropologist
- Date published:
- Date modified:
- Date accessed: December 26, 2025
- Link: https://askananthropologist.asu.edu/stories/brief-history-history
APA Style
Benjamin Schoville. (). A Brief History of History. Retrieved 2025, Dec 26, from {{ view_node }}
American Psychological Association, 6th ed., 2nd printing, 2009.
For more info, see the
APA citation guide.
Chicago Manual of Style
Benjamin Schoville. "A Brief History of History." ASU - Ask An Anthropologist. Published . Last modified . https://askananthropologist.asu.edu/stories/brief-history-history.
Chicago Manual of Style, 17th ed., 2017.
For more info, see the
Chicago Manual citation guide.
MLA Style
Benjamin Schoville. A Brief History of History. ASU - Ask An Anthropologist. , {{ view_node }}. Accessed December 26, 2025.
Modern Language Association, 8th ed., 2016.
For more info, see the
MLA citation guide.
Be Part of
Ask An Anthropologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a volunteers page to get the process started.

