
Human limbs
Humans may learn to walk by crawling on hands and feet, but it would seem a bit odd if adult humans were walking around on their hands and feet. Unlike other primates, human hands are not used for walking. Because of this they are adapted to other tasks. Our wrists and thumbs are very mobile and are particularly well-suited to making tools.
We rely on only our legs for walking and running. Therefore, our legs are relatively longer than our arms. Other primates rely on their arms for movement, like gibbons, and have much shorter legs than arms.
Our leg bones are also adapted to bipedal walking. The thigh bone, or femur, is angled inward. This angle brings your knees closer together, right under your upper body, making you more stable on two legs.
The human foot is also adapted to walking on two legs. Most primates have a big toe that is far away from the other toes. In humans, the big toe is in line with the rest of the toes. Its position and large size allow us to use all five toes to push off the ground when we walk.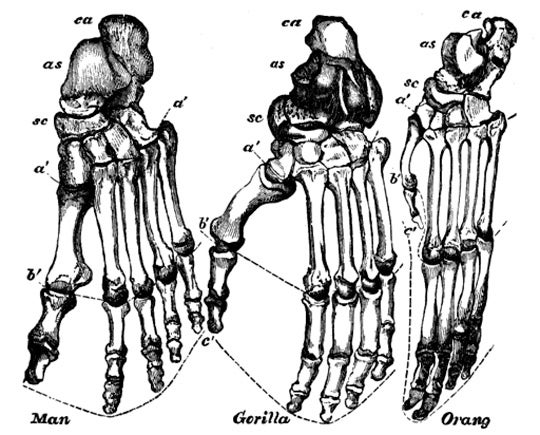

Our lower limbs are specially suited to walking on only two legs. The inward angle of the femur allows us to balance better.
Image by Jecowa.
Be Part of
Ask An Anthropologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a volunteers page to get the process started.
